For centuries, architecture has thrived on the collaboration between diverse professionals—architects, engineers, specialty designers, and urban planners. This collective effort has driven the evolution of architectural design, blending artistic vision with technical precision. As we advance into the digital age, a new player has entered the field: artificial intelligence (AI). The advent of AI introduces a powerful new element to this collaboration, one that can generate creative solutions, optimize complex processes, and analyze data with unprecedented speed and accuracy. AI’s integration into architectural design represents more than a technological upgrade. It signifies a transformative shift in conceptualizing and constructing buildings and cities. Architects now have a friend to explore various design possibilities through generative algorithms, which can propose innovative solutions that might otherwise remain undiscovered. AI is a facilitator in this context, helping architects create more sustainable and user-centric designs by analyzing environmental data and user needs. This emerging paradigm underscores the importance of human-AI cooperation in achieving groundbreaking results in architecture.

This collaboration between human creativity and machine intelligence promises numerous benefits, such as enhanced creativity, increased efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. AI’s ability to handle routine tasks and complex calculations allows architects to focus on the creative aspects of their work. More importantly, AI’s role in optimizing complex processes is reassuring, as it can propose innovative solutions that might otherwise remain undiscovered. Moreover, AI’s ability to process and analyze large datasets enables more informed and sustainable design choices. The benefits of AI in architecture are significant, but integrating AI into the architectural workflow has its challenges. Ensuring that AI complements rather than replaces human creativity is crucial. Ethical considerations regarding the use of AI, such as transparency, accountability, and the potential for bias, must be addressed to maintain trust and integrity in the design process. Exploring the evolution of collaborative design, examining the benefits and challenges of AI integration, and showcasing successful case studies can provide a comprehensive understanding of how AI is reshaping architecture. Understanding the tools and technologies enabling this collaboration and anticipating future trends will help professionals navigate this evolving landscape effectively, revealing a future where buildings and cities are more innovative and efficient but more responsive to their inhabitants’ needs.
The Evolution of Collaborative Design
Collaborative design has evolved significantly over the years. Traditionally, it involved manual drafting and in-person teamwork. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) revolutionized the field by allowing for digital collaboration. As CAD technology advanced, it incorporated 3D modeling and Building Information Modeling (BIM), further enhancing collaborative efforts.
The next significant leap came with the integration of AI. AI-driven tools can now analyze complex datasets, generate design alternatives, and optimize various aspects of architectural projects. This evolution from manual to AI-assisted design represents a paradigm shift, where architects and AI systems work together to achieve outcomes that neither could accomplish alone.
Benefits of Human-AI Cooperation in Architecture
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
AI has the potential to revolutionize the creative process in architecture. AI can generate unique design ideas by analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns that might not be immediately apparent to humans. For instance, Autodesk’s Dreamcatcher system allows designers to input specific design goals and constraints, generating multiple design alternatives. This approach fosters innovation by presenting options that human designers might have yet to consider. Moreover, AI can facilitate creative exploration by suggesting novel materials, structural solutions, and spatial configurations that align with the project’s goals. This agility is a promising sign for the future of architecture, where AI can catalyze unprecedented creativity and innovation.
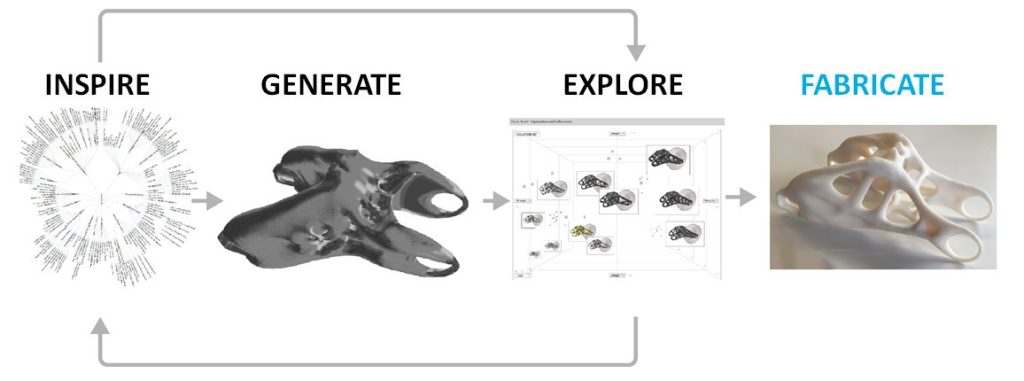
Studies have shown that AI can significantly enhance design creative output. A survey conducted by McKinsey & Company found that 45% of architectural firms using AI reported improved creativity and innovation in their projects. By leveraging AI’s ability to process and analyze large volumes of data, architects can explore a broader range of design possibilities, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
Efficiency and Productivity In Human-AI Cooperation
Through human-AI cooperation, AI can significantly streamline architecture workflows. AI-powered tools like Spacemaker AI can rapidly analyze site conditions, zoning regulations, and other factors to propose optimal site layouts, thereby reducing the time spent on initial design stages. In addition, AI can automate repetitive tasks such as drafting, freeing up architects to focus on more complex aspects of the design process. This convenience reassures us that AI is a creative partner and a reliable assistant, helping architects work more efficiently and productively.
The impact of AI on productivity is evident in various case studies. A report by Deloitte highlighted that firms integrating AI into their design processes experienced a 14% increase in productivity through human-AI cooperation. This efficiency boost accelerates project timelines and allows firms to take on more projects simultaneously, increasing their overall capacity and revenue potential.
Dependable Data-Driven Decision Making
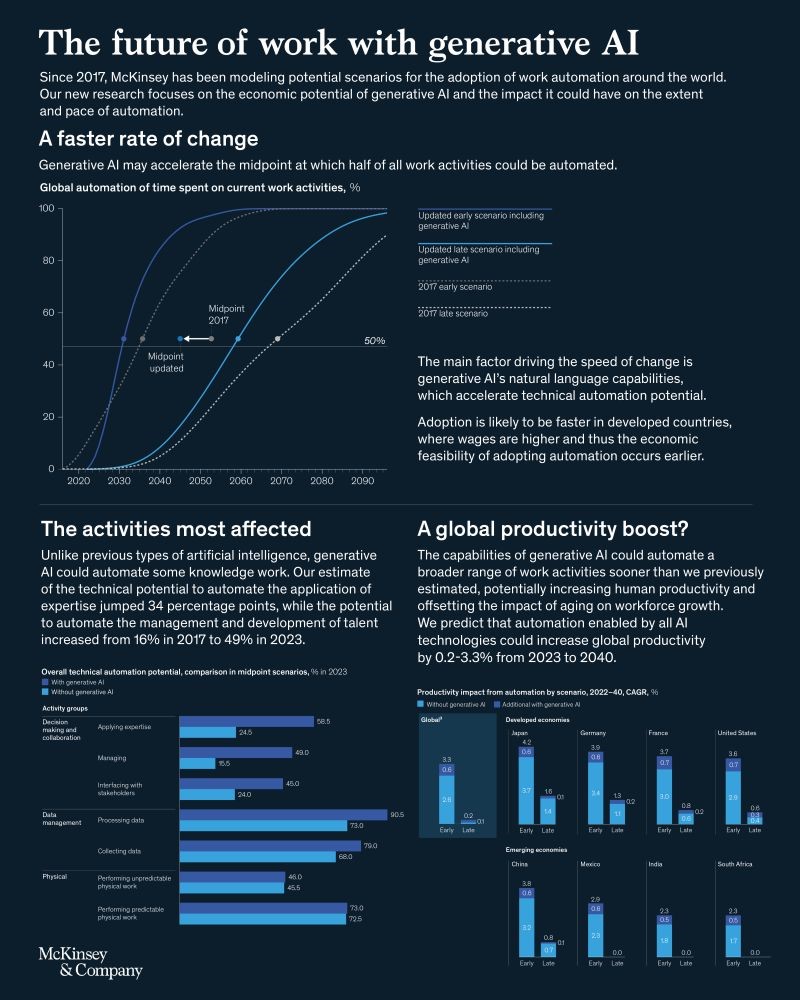
AI’s ability to analyze large datasets and inform design decisions is a game-changer for architecture. By optimizing building energy performance through simulating various scenarios and selecting the most energy-efficient design, AI can accurately lead to more sustainable and efficient buildings. Predictive analytics can help architects anticipate potential issues and make informed decisions to mitigate risks. This confidence in AI’s ability to make data-driven decisions is a significant step towards a more sustainable and efficient future for architecture.
One of the significant advantages of data-driven design is its ability to enhance sustainability. AI can analyze environmental data, such as sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and temperature fluctuations, to optimize building orientation and materials. This results in designs that minimize energy consumption and environmental impact. Research published in the Journal of Building Performance Simulation demonstrated that AI-optimized designs could reduce energy consumption by up to 40% compared to traditional methods.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Potential Loss of Human Touch In Collaborations
AI may eventually overshadow human creativity and intuition. To maintain a balance, we should treat AI as a tool that enhances rather than replaces human input. Architects must keep their creative vision at the center of the design process. The scope involves establishing clear guidelines for AI use and continuously iterating on designs to incorporate human insights.
To address these concerns, architectural firms adopt hybrid approaches where AI assists in the initial design stages, and human architects refine and finalize the designs. This collaborative approach ensures that AI enhances, rather than diminishes, human creativity. Additionally, firms are investing in training programs to help architects develop skills in AI integration, ensuring they can effectively leverage AI tools without compromising their creative vision.
Ethical and Legal Issues Governing Human-AI Partnership
Intellectual property concerns arise with AI-generated designs. For example, who owns the rights to AI-created designs? Additionally, the industry must discuss ethical considerations about the reliance on AI for significant design decisions. Transparency in AI algorithms and processes is essential to build trust and accountability.
Legal frameworks for AI-generated content are still evolving. Architects and firms must stay informed about the latest regulations and best practices to navigate these complexities. Collaborating with legal experts specializing in intellectual property and AI can help mitigate risks and ensure compliance. Additionally, industry organizations, such as the American Institute of Architects (AIA), are developing guidelines to address ethical and legal issues related to AI in architecture.
The Importance of Transparency In Human-AI Cooperation
Maintaining trust by ensuring transparency in AI algorithms and design processes benefits human-AI cooperation. Architects should have a clear understanding of how AI systems make their recommendations and be able to explain these processes to clients and stakeholders, fostering confidence in AI-assisted designs and promoting informed decision-making. The academic community should embrace this technology to educate designers about AI and understand its workings even at programming levels, promoting intimacy and strengthening human-AI cooperation.
Examples Of Successful Human-AI Collaborations
Autodesk and Van Wijnen On Generative Urban Design
The collaboration between Autodesk and Van Wijnen exemplifies the powerful potential of human-AI cooperation in architecture and urban planning. This partnership began in late 2016, when Van Wijnen, an innovative Dutch construction company, sought to reinvent its approach to building homes by applying generative design at an urban scale. Generative design is a method where AI algorithms generate various design solutions based on defined constraints and goals.
Autodesk Research’s in-house architectural studio, The Living, led this project. They utilized advanced AI tools like Dynamo and Refinery to create complex urban layouts that balanced various financial, sociological, and environmental metrics. This generative design approach allowed for optimizing residential area layouts, ensuring that the outcome met multiple stakeholder requirements simultaneously.
The process began by defining specific goals and constraints for the urban designs, such as the number and location of access streets, setbacks, parking regulations, and the mix of residential units. The AI tools then generated numerous design iterations, which were evaluated and refined based on these criteria. This method enabled a comprehensive exploration of design possibilities, leading to more informed and effective urban planning decisions.
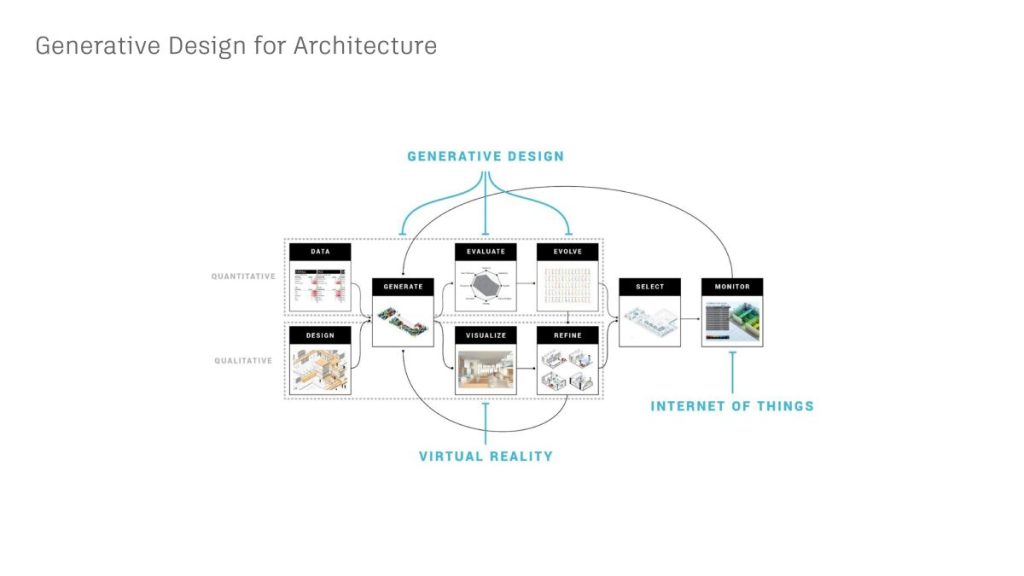
This collaboration highlighted several vital benefits of human-AI partnerships; AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and generate numerous design alternatives provided architects and planners with a broader spectrum of options to consider. Moreover, the iterative feedback loop between human designers and AI systems ensured that the final designs were innovative, practical, and well-suited to real-world conditions.
Spacemaker AI in Urban Planning
Spacemaker AI has been used in urban planning projects to optimize site layouts. One notable project involved the development of a new urban district, where Spacemaker analyzed environmental factors, noise pollution, and sunlight exposure to propose an optimal layout that maximized livability and sustainability. The project resulted in a highly efficient and environmentally friendly urban plan that received acclaim from stakeholders and residents.
Spacemaker AI in this project demonstrates how human-AI cooperation can enhance urban planning by providing data-driven insights that inform design decisions. This case study highlights the potential for AI to create more sustainable and livable urban environments, addressing the growing demand for smart city solutions.
Spacemaker.ai, a Norway-based startup specializing in AI-driven urban design software, was acquired by Autodesk in November 2020 for approximately $240 million. This acquisition was part of Autodesk’s strategy to enhance its portfolio in AI solutions for architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) sectors.
Founded in 2016, Spacemaker developed a platform that assists architects and developers in optimizing building designs by analyzing various site conditions and design scenarios. The software gained traction for its ability to significantly improve project outcomes, such as reducing planning phases and increasing property values through enhanced design options.
Post-acquisition, Spacemaker has continued to operate autonomously within Autodesk, focusing on its mission to innovate urban development processes. Integrating Autodesk’s ecosystem is expected to broaden Spacemaker’s reach, allowing it to serve a larger global customer base while maintaining its core functionality and user experience.
Tools and Technologies Enabling Human-AI Collaborative Design
Evolving AI Tools and Software
Several AI tools and software facilitate human-AI collaboration in architecture. The more advanced architectural industry widely uses tools like Autodesk’s Generative Design, Spacemaker AI, and AI-driven plugins for Rhino’s Grasshopper. These tools help architects explore design options, optimize site layouts, and improve building performance. Each tool offers unique features that cater to different aspects of the design process, from initial concept generation to detailed analysis and optimization.
Autodesk’s Generative Design, for instance, allows architects to input specific design goals and constraints, and the software generates a multitude of design alternatives. This capability enables architects to explore diverse possibilities and identify the most effective solutions. Spacemaker AI, on the other hand, focuses on urban planning and site analysis, providing insights into environmental factors and optimizing layouts for sustainability and livability.
AI is revolutionizing the AEC industry through various innovative tools and platforms. Advanced software like TestFit, Giraffe, and Spacemaker AI are revolutionizing how architects and urban planners approach design by optimizing resources, analyzing environmental factors, and generating multiple design alternatives. These AI-driven solutions streamline workflows, enhance project feasibility studies, and promote sustainable and user-centric designs. Additionally, platforms such as Veras and Project Dreamcatcher leverage AI for generative design and high-quality visualizations, significantly boosting creativity and efficiency in architectural practices.
Integration Tips And Workflow
Integrating AI tools into existing workflows requires a strategic approach. Architects should start with pilot projects to understand the tool’s capabilities and limitations. Training sessions and workshops can help team members proficiently use these tools. Collaboration with AI specialists can bridge knowledge gaps and ensure effective tool integration.

Firms should consider establishing dedicated AI teams or roles within their organizations to facilitate successful integration. These teams can focus on exploring new AI technologies, conducting pilot projects, and providing training and support to other team members. Additionally, firms should encourage a culture of experimentation and continuous learning, where architects feel empowered to explore and adopt AI tools.
Future Prospects of Human-AI Collaborative Design
The future of collaborative design in architecture looks promising with continuous advancements in AI technology. Future AI developments include more intuitive design interfaces, improved predictive analytics, and enhanced capabilities for real-time collaboration. Architects must stay updated with these trends and continuously learn to leverage AI effectively.
One exciting prospect is the development of AI systems that can understand and respond to human emotions and preferences. This evolution could lead to more personalized and human-centric designs that cater to clients’ and end-users’ specific needs and desires. Additionally, advancements in machine learning algorithms and data analytics will enable AI to provide even more accurate and insightful recommendations, further enhancing human-AI cooperation.